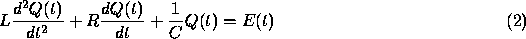



One of the more obvious classifications is based on whether the unknown function depends on a single independent variable or on several independent variables. In the first case only ordinary derivatives appear in the differential equation, and it is said to be an ordinary differential equation. In the second case the derivatives are partial derivatives, and the equation is called a partial differential equation.
Two examples of ordinary differential equations, in addition to Eq. (1), are
for the charge 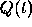 on a capacitor in a circuit with capacitance C,
resistance R, inductance L, and impressed voltage
on a capacitor in a circuit with capacitance C,
resistance R, inductance L, and impressed voltage 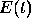 ;
and the equation governing the decay with time of an amount
;
and the equation governing the decay with time of an amount 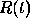 of
a radioactive substance, such as radium,
of
a radioactive substance, such as radium,
where k is a known constant. Typical examples of partial differential equations are the potential equation (also called Laplace's equation)
the diffusion or heat conduction equation
and the wave equation
Here 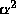 and
and 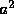 are certain constants. The potential
equation, the diffusion equation, and the wave equation arise in a variety
of problems in the fields of electricity and magnetism, elasticity, and fluid
mechanics. Each is typical of distinct physical phenomena (note the
names), and each is representative of a large class of partial differential
equations.
are certain constants. The potential
equation, the diffusion equation, and the wave equation arise in a variety
of problems in the fields of electricity and magnetism, elasticity, and fluid
mechanics. Each is typical of distinct physical phenomena (note the
names), and each is representative of a large class of partial differential
equations.